Stroke: what is it and how to prevent ?
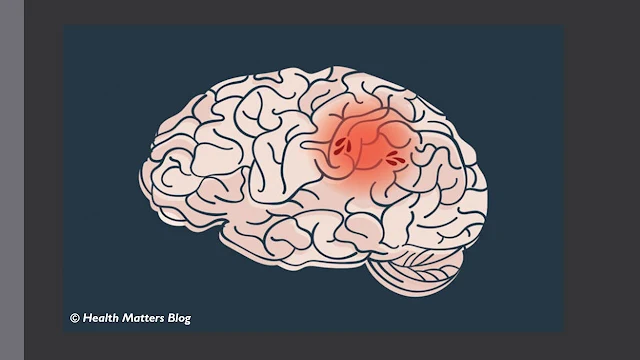 |
| Stroke occurs occurs when blood supply to the brain is interrupted resulting into damage to the brain tissue affected. |
Stroke is a serious medical condition that can cause long-term disability or even death. It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either by a clot or a burst blood vessel. This can cause damage to the brain tissue, which can lead to a wide range of physical and cognitive problems. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of stroke.
Causes of Stroke:
There are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Ischemic stroke is caused by a blood clot that blocks the flow of blood to the brain, while hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a burst blood vessel in the brain.
Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, accounting for around 87% of all cases. The blood clots that cause ischemic stroke can form in the brain itself or in other parts of the body and travel to the brain. The most common risk factors for ischemic stroke include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, atherosclerosis, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a family history of stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke is less common but more deadly than ischemic stroke. It occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding into the brain tissue. The most common risk factors for hemorrhagic stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, alcohol use, and a family history of stroke.
Symptoms of Stroke:
The symptoms of stroke can vary depending on which part of the brain is affected. The most common symptoms of stroke include:
Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding speech.
Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes.
Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or trouble walking.
Sudden severe headache with no known cause.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Time is critical when it comes to stroke, and the faster the person can receive treatment, the better their chances of recovery.
Diagnosis of Stroke:
If a stroke is suspected, the first step is to perform a physical exam and gather information about the person's medical history and symptoms. Imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI can also help to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of stroke.
Blood tests may also be done to check for factors that can increase the risk of stroke, such as high cholesterol, diabetes, and blood clotting disorders.
Treatment of Stroke:
The treatment of stroke depends on the type and severity of the stroke, as well as the person's overall health and medical history. In general, the goals of treatment are to restore blood flow to the brain, prevent further damage, and reduce the risk of future strokes.
For ischemic stroke, the most common treatment is a clot-busting drug called tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). This drug is most effective when given within 4.5 hours of the onset of symptoms, so it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
If tPA is not an option, other treatments may include mechanical clot removal, antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications, and surgery to remove blockages in the arteries.
For hemorrhagic stroke, the goal of treatment is to stop the bleeding and reduce pressure on the brain. This may involve medication to control blood pressure, surgery to remove the blood clot, or a procedure to repair the damaged blood vessel.
Rehabilitation is also an important part of stroke treatment, especially for those who have suffered long-term disability. This may include physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and other types of support to help the person regain function and independence.
Prevention of stroke:
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of stroke:
1-Manage your blood pressure: High blood pressure is the single biggest risk factor for stroke, so it is important to keep your blood pressure within a healthy range. This may involve making lifestyle changes such as reducing salt intake, losing weight, and exercising regularly, as well as taking medication if necessary.
2-Control your cholesterol levels: High cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can increase the risk of stroke. Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly can help to keep cholesterol levels in check, as can taking medication if necessary.
3-Quit smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of stroke, so it is important to quit if you are a smoker.
4-Manage diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of stroke, so it is important to manage diabetes through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary.
5-Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help to lower blood pressure, control cholesterol levels, and maintain a healthy weight, all of which can reduce the risk of stroke.
6-Eat a healthy diet: Eating a diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein and low in saturated and trans fats can help to reduce the risk of stroke.
7-Limit alcohol intake: Drinking too much alcohol can increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke, so it is important to limit alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
8-Treat atrial fibrillation: Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition that can increase the risk of stroke, so it is important to treat it with medication or other interventions if necessary.
By following these steps, you can reduce your risk of stroke and improve your overall health and well-being



Comments
Post a Comment
your comments are appreciated